Table of Contents
ToggleIn a world where data breaches are as common as cat videos, blockchain servers are stepping in like a superhero in a cape. They promise to revolutionize how we store and share information, making it safer and more transparent. Imagine a digital fortress that not only guards your data but also lets you peek inside whenever you want—no secret passwords or hidden keys required.
What Are Blockchain Servers?
Blockchain servers enable secure data storage and sharing through decentralized networks. These servers utilize blockchain technology to enhance the transparency and integrity of data.
Definition and Functionality
Blockchain servers serve as the backbone of decentralized applications by maintaining a distributed ledger. They process transactions while ensuring data integrity through cryptographic techniques. Each server contributes to the network, validating and recording transactions. These servers eliminate reliance on central authorities, thus promoting peer-to-peer interactions. Users can access data quickly while benefiting from the inherent security features of blockchain technology.
Comparison with Traditional Servers
Traditional servers rely on centralized systems to manage data storage and processing. Unlike traditional servers, blockchain servers distribute data across multiple nodes, enhancing security. Centralized servers create vulnerabilities, whereas decentralized architecture significantly reduces risks like data breaches. Transparency varies; blockchain servers provide a public ledger accessible to all participants, enabling real-time accountability. Costs also differ; maintaining traditional servers often incurs high operational expenses, while blockchain solutions can optimize resource allocation.
Types of Blockchain Servers
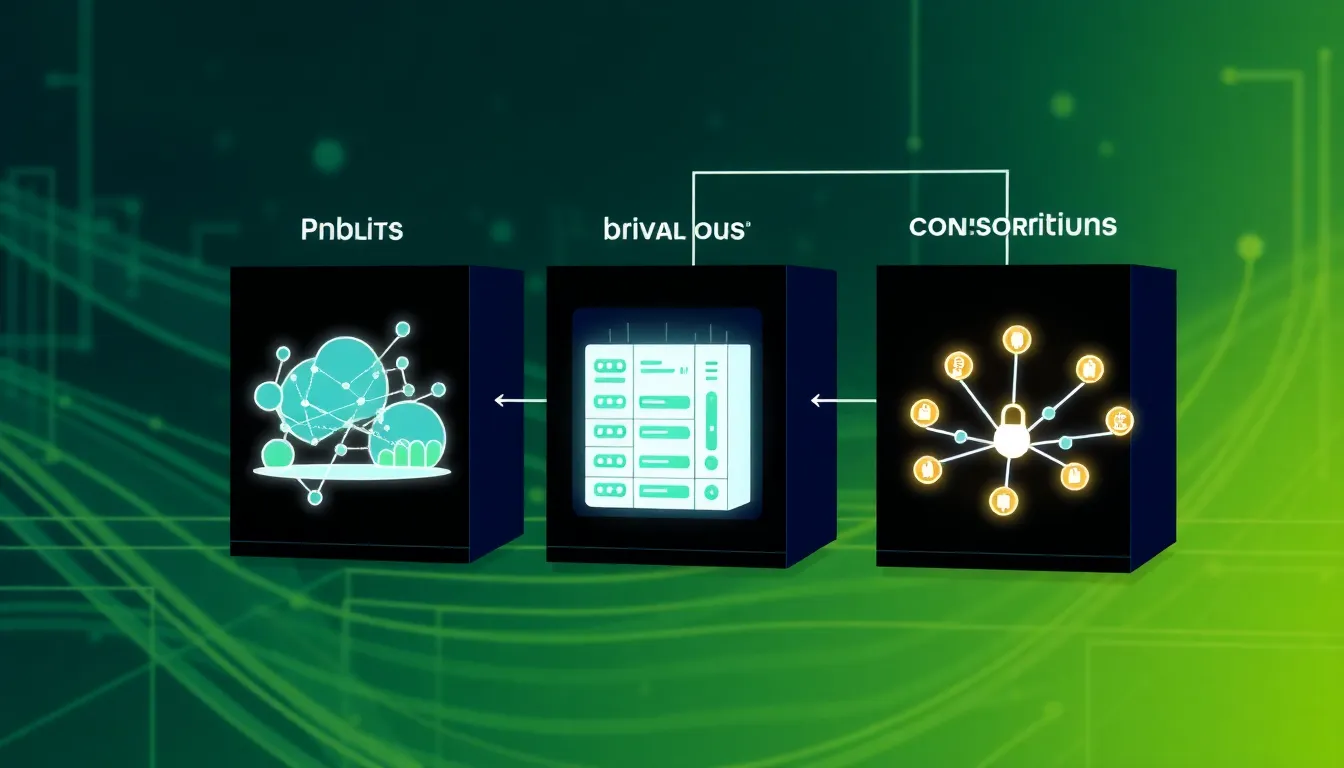
Blockchain servers come in three primary types: public, private, and consortium. Each type serves distinct purposes and caters to different organizational needs.
Public Blockchain Servers
Public blockchain servers operate on decentralized networks accessible to anyone. These servers enable anyone to participate in transaction validation and network governance, enhancing transparency and security. Examples include Bitcoin and Ethereum, which allow users to verify transactions without intermediaries. Anyone interested in cryptocurrencies can interact directly with these platforms. Their open nature fosters innovation through development of decentralized applications. Developers and users leverage the public ledger to facilitate trust among peers.
Private Blockchain Servers
Private blockchain servers restrict access to authorized users within a specific organization. These servers maintain control over transaction validation and data visibility, focusing on security and privacy. Companies often utilize private blockchains for internal operations and data management. For instance, IBM’s Hyperledger Fabric streamlines supply chain processes by providing a secure environment for data sharing among partners. Private servers offer speed and efficiency, as only approved participants can access the network. Organizations prioritize confidentiality while enjoying the benefits of blockchain technology.
Consortium Blockchain Servers
Consortium blockchain servers involve multiple organizations sharing control of a network. These servers balance decentralization with a controlled environment, typically seen in industries with shared interests. Members work collaboratively to validate transactions, enhancing trust among participants. An example is the R3 Corda platform, which connects financial institutions for secure interactions without exposing sensitive data. Consortium models promote collaboration and efficiency while benefiting all parties involved. Organizations focusing on joint ventures find consortium blockchains particularly advantageous.
Benefits of Using Blockchain Servers
Blockchain servers provide numerous advantages in data management. These benefits significantly enhance the way organizations handle data and foster interactions.
Enhanced Security
Blockchain servers enhance security through their decentralized nature. Without a single point of failure, vulnerabilities decrease, making it difficult for hackers to compromise data. Each transaction undergoes cryptographic validation, ensuring data integrity. Additionally, the immutability of the blockchain records protects against unauthorized modifications. Data breaches become less likely, providing organizations with peace of mind. Examples of successful cybersecurity applications include financial institutions adopting blockchain to safeguard transaction data securely.
Improved Transparency
Transparency improves significantly with blockchain servers. A public ledger maintains a record of all transactions visible to participants. Stakeholders can independently verify transactions, fostering trust among users. This level of transparency eliminates the need for intermediaries, which can delay processes and increase costs. Organizations in supply chains benefit from tracking product origins and movement in real-time, enabling quick access to information. As seen in industries like finance and healthcare, transparency leads to stronger relationships built on trust and accountability.
Increased Efficiency
Efficiency increases when using blockchain servers for data handling. Automation through smart contracts streamlines processes by executing predefined conditions without human intervention. Data exchanges occur directly between parties, reducing time spent on transactions. Increased speed results in quicker decision-making, benefiting industries like logistics and retail. Organizations save on operational costs due to the elimination of intermediaries and reduced paperwork. Effective resource allocation emerges from this optimization, creating a more agile business environment which enhances overall productivity.
Challenges and Considerations
Blockchain servers present unique challenges that users must navigate. These include scalability issues, energy consumption, and regulatory compliance.
Scalability Issues
Scalability concerns arise as more users join the blockchain network. Transaction speed often diminishes under high volume, leading to delays and higher fees. Solutions, such as sharding and layer-two protocols, help alleviate these issues but may introduce complexity. Integrating these enhancements requires careful planning to maintain network performance. Without addressing scalability, user experience can suffer, hindering adoption and application growth.
Energy Consumption
Energy consumption represents a significant drawback of blockchain technology, particularly for public networks like Bitcoin. The proof-of-work consensus mechanism demands substantial computational power, resulting in high energy usage. Alternative consensus methods, like proof-of-stake, promise reduced energy requirements while maintaining security. Adopting sustainable practices is crucial as concerns about environmental impact grow. Organizations need to evaluate energy-efficient options when deploying blockchain solutions.
Regulatory Compliance
Regulatory compliance poses ongoing challenges for blockchain servers. Governments increasingly scrutinize cryptocurrencies and decentralized applications due to potential risks of fraud and money laundering. Organizations must navigate varying regulations across jurisdictions. A proactive approach to compliance can avert legal complications and promote trust among users. Staying informed about regulatory changes remains essential as the blockchain landscape evolves rapidly.
Blockchain servers represent a significant advancement in data management technology. By decentralizing data storage and sharing, they enhance security and transparency while reducing vulnerabilities inherent in traditional systems. Their ability to support various types of networks—public, private, and consortium—ensures that organizations can tailor solutions to meet specific needs.
Despite challenges like scalability and energy consumption, the potential benefits far outweigh the drawbacks. As businesses increasingly adopt blockchain technology, they’ll likely experience improved efficiency and trust in their operations. Staying ahead of regulatory changes will be crucial for organizations looking to leverage these innovative solutions effectively. The future of data management is undoubtedly leaning towards blockchain servers, paving the way for a more secure and efficient digital landscape.







